Question 58 DDE01 - Designated Duty Engineer - Unlimited HP
The freshwater cooling systems serving the main engines of your towing vessel are of the type shown in the illustration. What statement accurately describes the characteristics of the freshwater cooling circuit? Illustration MO-0137
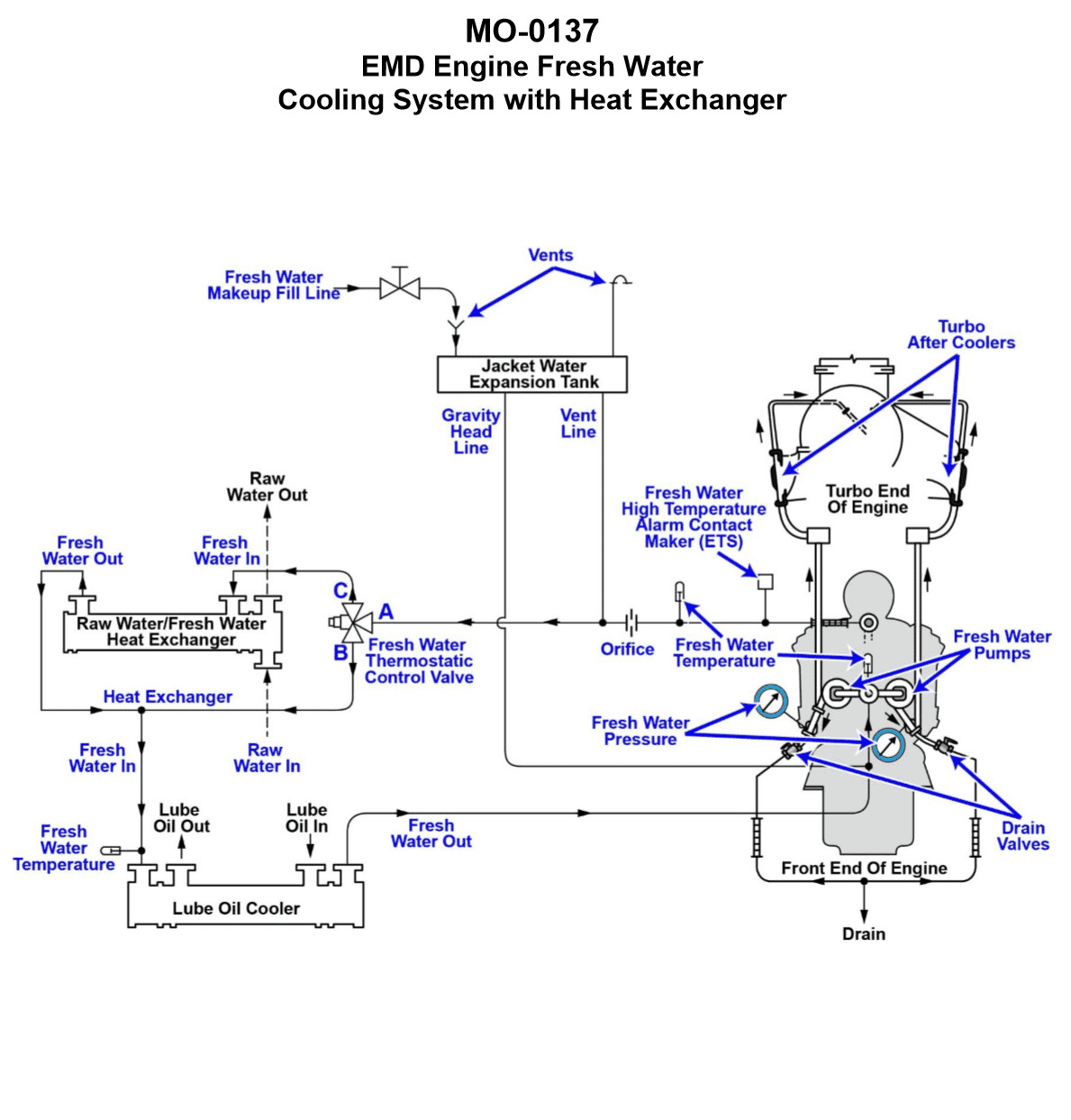
The Correct Answer is A **Explanation for Option A (Correct Answer):** Option A states, "The freshwater circuit is a vented system using a stationary/marine type 3-way thermostatic control valve for temperature control." 1. **Vented System:** Marine cooling systems, particularly those serving large main engines and utilizing heat exchangers (as implied by the context of a towing vessel's main engine cooling illustration, like MO-0137), are typically designed to operate slightly above atmospheric pressure but are considered "vented." They rely on an expansion tank located above the system, which allows the coolant to expand and contract freely and includes an open vent (or an overflow line leading to a vented tank) to release trapped air and prevent high pressures that could damage heat exchangers or seals. While some modern systems are fully pressurized, traditional heavy-duty marine engine cooling circuits are commonly vented. 2. **Stationary/Marine Type 3-Way Thermostatic Control Valve:** Temperature control in these heavy-duty marine installations requires precise and continuous modulation of flow to maintain a stable engine block temperature. A 3-way thermostatic valve (often called a regulating valve, or sometimes a self-actuated regulating valve, or 'AMOT' type valve after a common manufacturer) is essential for this purpose. This valve works by continuously sensing the engine outlet water temperature and proportioning the flow: it directs some hot water through the heat exchanger (for cooling) and bypasses the rest directly back to the engine intake. This mixing action maintains the exact desired temperature, which is characteristic of robust, stationary, and marine engine installations. **Explanation for Incorrect Options:** * **B) The freshwater circuit is a pressurized system using a stationary/marine type 3-way thermostatic control valve for temperature control.** * **Incorrect:** While the 3-way valve is correct for temperature control, describing the system as "pressurized" (like an automotive system operating under high pressure cap control) is generally inaccurate for the standard, traditional heavy-duty marine cooling circuit shown in typical illustrations like MO-0137, which is usually vented via an expansion tank to the atmosphere or a low-pressure overflow tank. * **C) The freshwater circuit is a vented system using an automotive type 2-way thermostatic control valve for temperature control.** * **Incorrect:** The 2-way (or conventional poppet style) thermostat used in automotive applications is designed simply to block flow until the operating temperature is reached, then fully open. It does not provide the sophisticated, proportional mixing (bypassing and cooling) required to maintain the tight temperature tolerances necessary for large marine engines operating continuously under varying loads. The required component is a 3-way valve. * **D) The freshwater circuit is a pressurized system using an automotive type 2-way thermostatic control valve for temperature control.** * **Incorrect:** This option incorrectly identifies both the system type ("pressurized" instead of vented) and the valve type (2-way automotive instead of 3-way marine/stationary).
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app