Question 33 DDE01 - Designated Duty Engineer - Unlimited HP
The escort tug to which you are assigned is fitted with hydraulic clutches similar to that shown in the illustration. If the time required for the clutch to disengage is unacceptably long, which of the following conditions would most likely be responsible for this? Illustration MO-0089
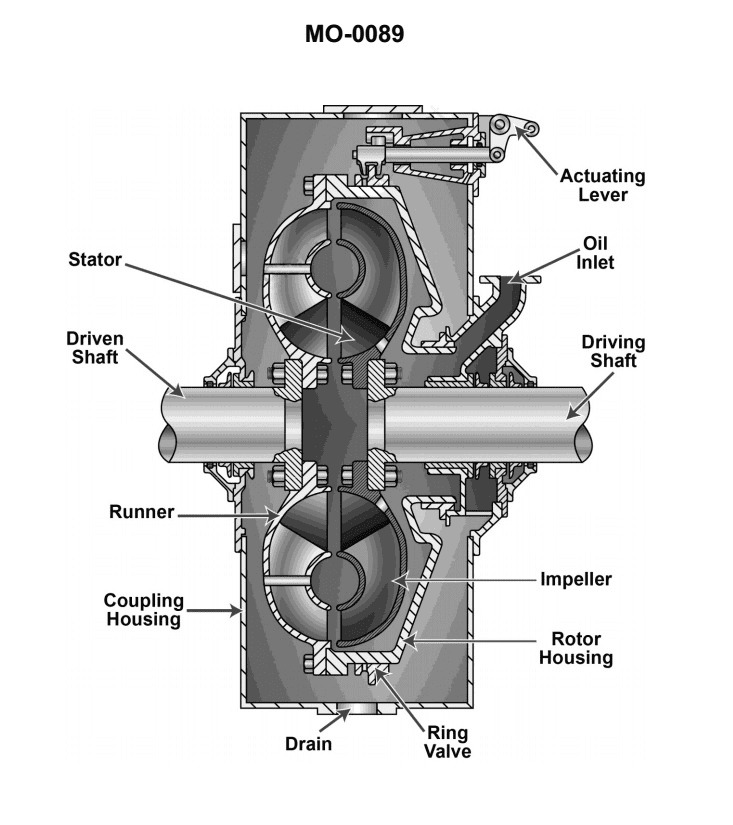
The Correct Answer is D **Why option D ("Solid contaminants are present in the hydraulic fluid.") is correct:** Hydraulic clutches, especially those used in marine applications like escort tugs, rely on precisely controlled hydraulic flow to engage and disengage quickly. When solid contaminants (dirt, metal particles, sludge) are present in the hydraulic fluid, they tend to accumulate in critical areas. Specifically, contaminants can clog or restrict small orifices, narrow passages, or precise control valves (like solenoid valves or relief valves) within the clutch actuating system. This restriction slows down the rate at which fluid can be exhausted from the clutch piston chamber, significantly lengthening the time required for the clutch to fully disengage. **Why the other options are incorrect:** * **A) Clutch operating fluid is maintained at too low a temperature:** Low temperature typically increases fluid viscosity (thicker fluid). While very high viscosity can slow down initial engagement or overall response, the primary issue leading to **unacceptably long disengagement time** is usually a restriction in the exhaust path (clogging), not just general viscosity, although extremely low temperatures could contribute. However, contamination (D) is the classic and most likely culprit for restricted hydraulic exhaust flow. * **B) Fluid clutch sump level maintained at too high a level:** An overly high sump level generally leads to issues like foaming, aeration, or excessive pressure buildup within the closed system, but it does not directly restrict the exhaust flow path necessary for rapid clutch disengagement. * **C) Clutch operating fluid is maintained at too high a temperature:** High temperature decreases fluid viscosity (thinner fluid). Lower viscosity generally speeds up response time and does not typically cause the restrictive flow issues that result in an unacceptably long disengagement time. (High temperatures primarily risk seal degradation and fluid breakdown.)
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app