Question 48 DDE01 - Designated Duty Engineer - Unlimited HP
The harbor tug to which you are assigned has a main engine fuel system as shown in the illustration. Besides preventing the attached fuel oil pump and the hand priming fuel oil pump from discharging through the other, what other purpose do the anti-flood check valves serve? Illustration MO-0152
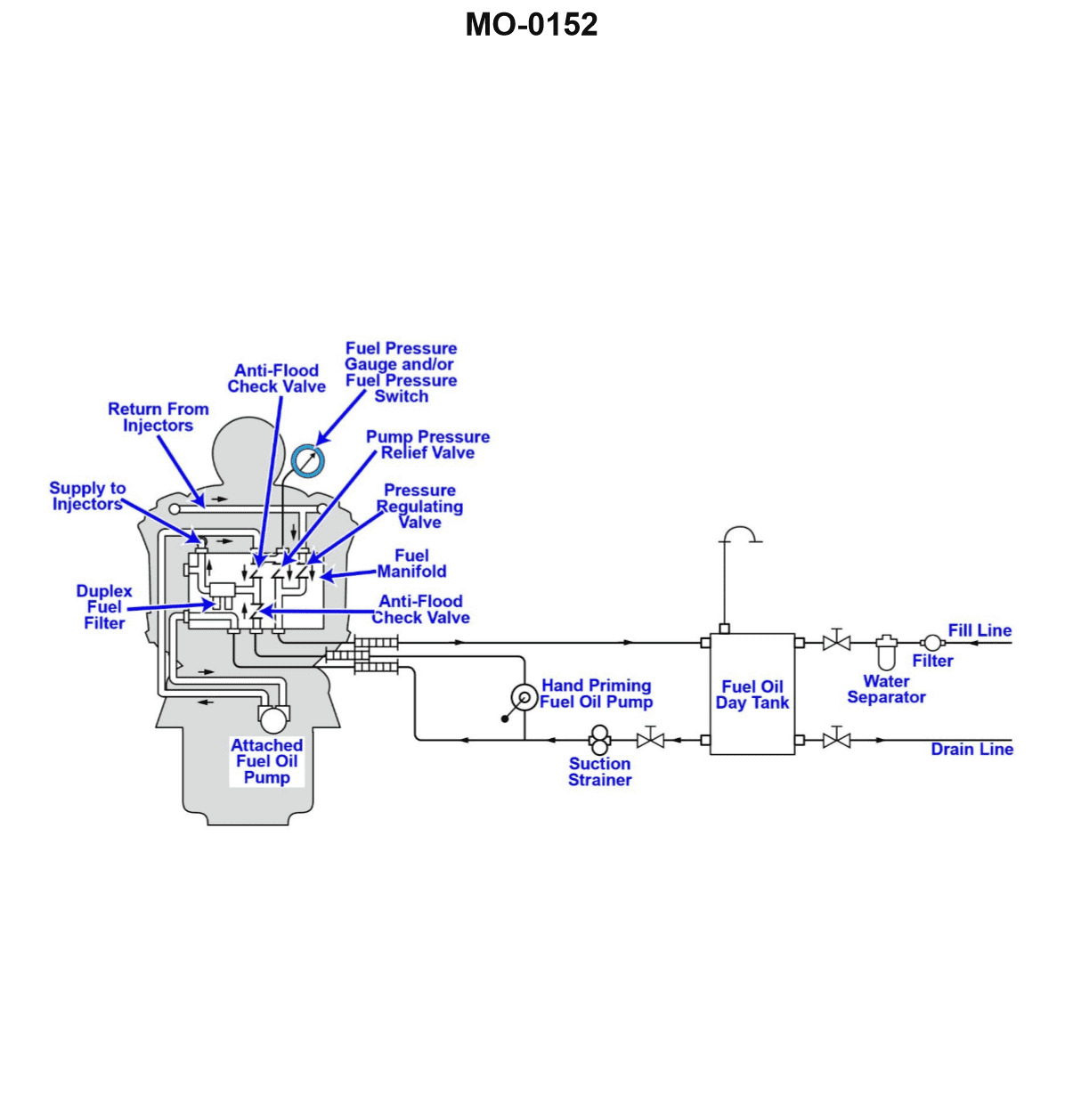
The Correct Answer is B **Explanation of why Option B is correct:** In a typical diesel engine fuel system setup, the anti-flood check valves (also commonly called anti-siphon valves or simply check valves) are essential components installed between the fuel pumps (main engine pump and priming pump) and the fuel supply line coming from the day tank. 1. **Preventing backflow when shut down:** When the engine is running, the main fuel pump maintains pressure and flow towards the engine. However, when the engine is shut down, flow stops. 2. **Day Tank Location Below the Engine (Suction System):** If the day tank is located *below* the engine (which is common in tugs and vessels where the engine is relatively high in the hull), the fuel system must lift the fuel from the tank up to the engine. If a leak or failure occurs anywhere in the high-pressure side of the engine (e.g., injector lines, filter housing), the fuel system could de-pressurize. Without the anti-flood check valves, the fuel inside the engine's supply lines, filters, and injection pump housing would drain back down through the pumps and into the day tank due to gravity, leading to a loss of prime (air inclusion) in the system. 3. **Purpose of Check Valves:** The anti-flood check valves, placed immediately after the pumps, ensure that once fuel has been drawn up and pressurized, it cannot drain back down into the suction line when the engine stops. This maintains the fuel prime, allowing the engine to start easily next time. **Explanation of why the other options are incorrect:** * **A) They prevent backflow of fuel from the engine to the day tank when the engine is shut down and when the day tank is located above the engine.** * *Incorrect Location/Function:* If the day tank is located **above** the engine (gravity feed system), the primary risk is not losing prime due to backflow drainage, but rather continuous forward flow (siphoning or flooding) due to gravity if a line breaks, which would require a shutoff valve, not just an anti-flood check valve primarily designed to maintain prime against gravity drain when the tank is below the engine. Furthermore, if the tank is above, gravity *helps* maintain prime, making the check valve's role in preventing back-drainage less critical for restart. * **C) They prevent backflow of fuel from the engine to the day tank when the engine is running and when the day tank is located above the engine.** * *Incorrect Operating State:* When the engine is running, the mechanical fuel pump is actively pushing fuel forward and maintaining positive pressure, making backflow highly unlikely (unless the pump fails). The primary function of maintaining prime using these valves is relevant when the engine is **shut down**. * **D) They prevent backflow of fuel from the engine to the day tank when the engine is running and when the day tank is located below the engine.** * *Incorrect Operating State:* As noted above, the engine's main pump prevents backflow while it is running. The critical function of the check valves is to maintain the lifted fuel column and prevent loss of prime when the engine is **shut down**.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app