Question 33 MODE02 - Assistant MODU Engineer
What prevents the thrust bearing blocks shown in the illustration from rotating within the housing? Illustration MO-0120
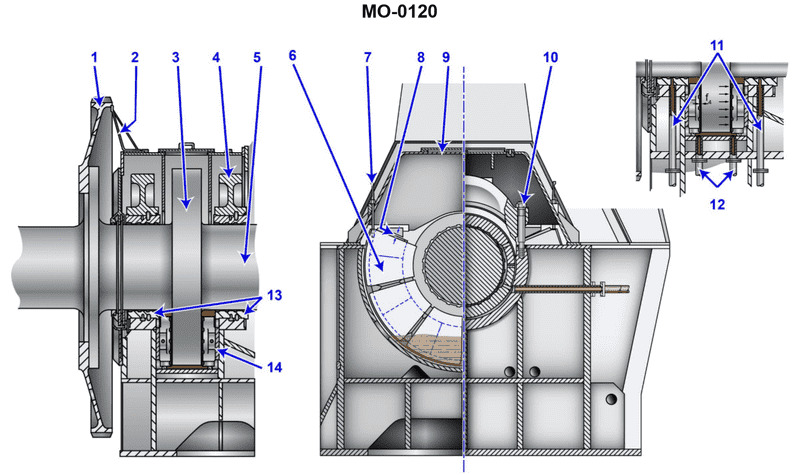
The Correct Answer is A. **Why Option A is Correct:** Option A describes the standard mechanical constraint mechanism used in many multi-segment or segmented thrust bearings (often referred to as Kingsbury or Mitchell type bearings). The bearing segments, or "shoes," must be held securely in place relative to the housing to transmit the axial load effectively without rotation. To achieve this, the housing, bearing cap, or cover incorporates specific features (like pins, dowels, keys, or extended protrusions) that fit into corresponding recesses or slots on the back of the thrust shoes. These protrusions prevent the thrust shoe segments from following the rotating shaft (rotation within the housing) while still allowing the critical tilting motion necessary for forming the hydrodynamic oil wedge. Maintaining the position also ensures the proper operational clearance is maintained. **Why the Other Options Are Incorrect:** * **B) The bearing blocks are massive and their weight provides sufficient force to prevent rotation.** This is incorrect. While thrust bearing components can be substantial, reliance on weight (gravity) alone is insufficient and unreliable for preventing rotation, especially given the high torque and oil film formation that effectively reduces friction. Mechanical keys or stops are always required. * **C) The thrust shoes are dovetailed into the collar.** This is incorrect. The thrust shoes (bearing segments) ride against the rotating collar (or runner). They must be secured to the **stationary housing**, not the rotating collar. If they were attached to the collar, they would rotate with the shaft and would not function as a stationary bearing surface. * **D) The bearing assembly is specifically designed to allow for rotation, permitting the transmittal of axial forces across a greater surface area and minimizing loading densities.** This is incorrect. The purpose of the **thrust shoes** is to provide a **stationary** surface against the rotating collar to transmit the axial force to the machine frame. Allowing the thrust shoes themselves to rotate would negate their function as a stationary bearing and prevent the proper formation of the critical hydrodynamic oil wedge necessary for operation.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app