Question 20 UFIV01 - Chief Engineer - UFIV
The mollusc dredger to which you are assigned has diesel generator engines fitted with intake and exhaust systems as shown in the illustration. What type of turbo charging configuration is used? Illustration MO-0176
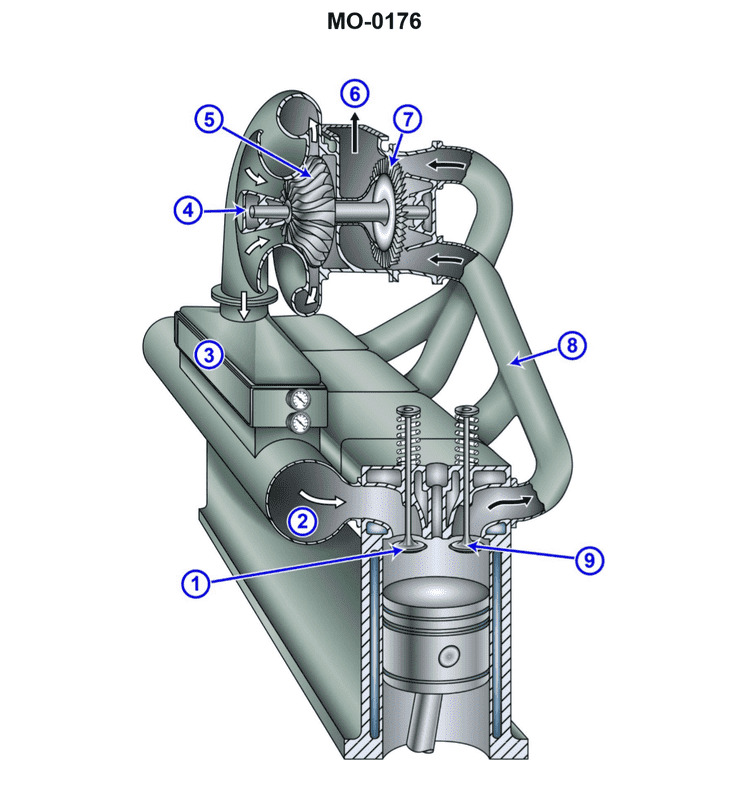
The Correct Answer is C ### 2. Explanation for Option C ("Pulse turbo charging") Pulse turbo charging (or pressure pulse turbo charging) is characterized by the manifold being divided into smaller, shorter sections that group cylinders based on their firing order. These separate sections lead directly to the turbine, often utilizing a multi-entry turbine casing. The primary purpose of this configuration is to preserve the high kinetic energy (pressure pulse) created immediately after the exhaust valve opens. By keeping the manifolds small and segregated, the energy in the pressure wave is not damped by interfering pulses from other cylinders. This system provides: 1. **Rapid Acceleration/Response:** The strong initial pulse provides immediate energy to spin up the turbocharger quickly. 2. **Good Efficiency at Low Load:** Unlike constant pressure systems, pulse charging maintains good efficiency and boost pressure even when the engine is operating at partial loads, which is essential for dredger operations that require frequent power changes and maneuvering. Since marine diesel generators, especially those operating under variable load conditions common on vessels like dredgers, historically prioritize low-load efficiency and rapid response, the illustration (MO-0176) would typically show the characteristic divided manifold structure associated with pulse charging. ### 3. Explanation for Incorrect Options **A) Constant pressure turbo charging:** This configuration uses a large, common exhaust manifold that collects the gas from all cylinders before it enters the turbine at a relatively steady pressure. While highly efficient at maximum load and continuous speed, it is inefficient and exhibits poor turbocharger response at low loads. If the illustration showed a single, large manifold, this would be the correct answer, but for systems prioritizing response (like those on variable-speed dredgers), pulse charging is usually depicted. **B) Boost-controlled turbo charging:** This is not a description of the core turbocharging configuration (manifold design). It is a method of controlling the maximum pressure delivered by the compressor, typically using a wastegate or variable geometry turbine (VGT). The fundamental arrangement of the exhaust manifold leading to the turbine would still be either pulse or constant pressure. **D) 2-stage turbo charging:** This system involves two separate turbochargers working in series (a low-pressure stage followed by a high-pressure stage) to achieve extremely high compression ratios. This configuration is highly complex and usually reserved for modern, high-performance engines needing maximum power density. It would be highly recognizable in the illustration due to the two distinct sets of compressors and turbines. Standard marine medium-speed diesel generators usually use single-stage turbocharging.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app