Question 18 QMED01 - Junior Engineer
What is the heat source for the deaerating feed tank introduced at "E" in the illustration? Illustration SG-0002
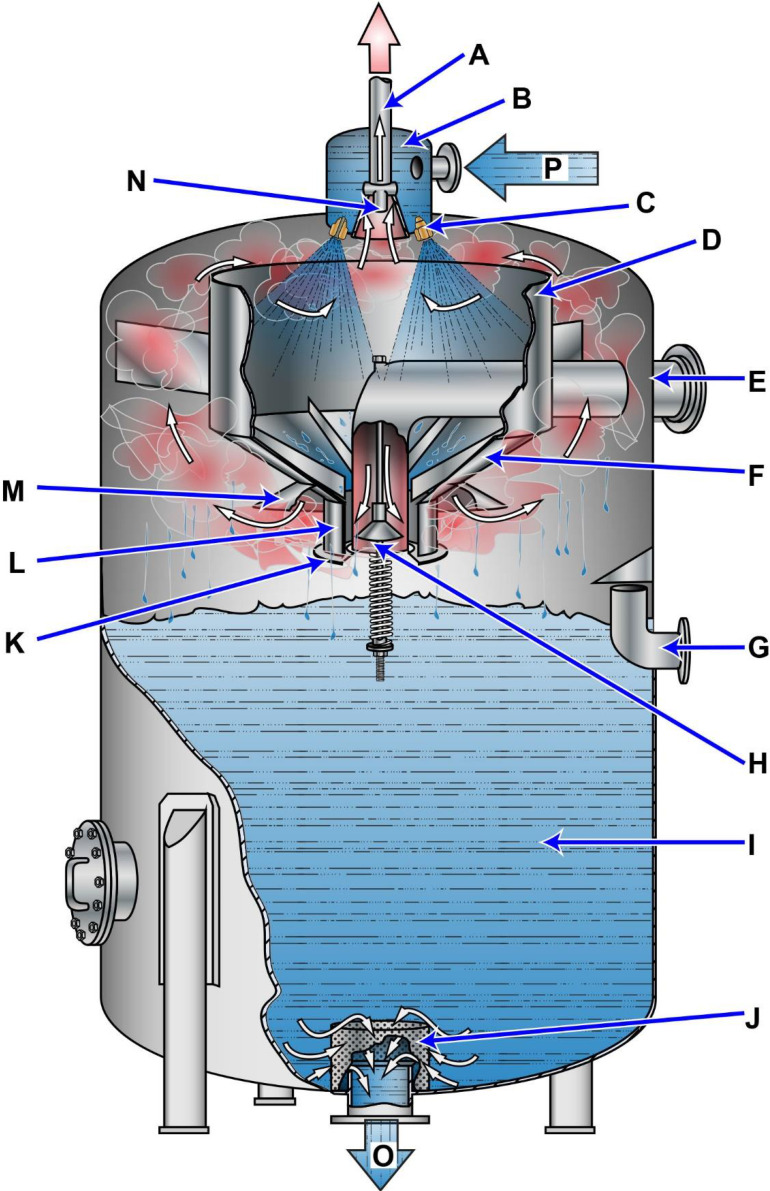
The Correct Answer is C **Explanation for Option C (Auxiliary exhaust steam):** The deaerating feed tank (often called a Deaerator or DFT) serves two primary functions in a steam cycle: heating the feedwater and removing dissolved gases (primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide) to prevent corrosion in the boiler and steam system. To achieve effective deaeration and heating, the water must be sprayed into a steam atmosphere. The heat source for the DFT in most marine or power plant installations, especially those utilizing exhaust steam, is the **auxiliary exhaust steam**. This steam is exhaust (or "waste") steam collected from various steam-driven auxiliary equipment (like feed pumps, forced draft blowers, turbogenerators, etc.) operating throughout the plant. Using auxiliary exhaust steam is highly efficient because it utilizes waste heat that would otherwise be rejected to the condenser, thus improving the overall thermal efficiency of the plant cycle. **Why the other options are incorrect:** * **A) High-pressure drains:** High-pressure drains (condensate recovered from devices like superheaters, HP heaters, or steam traps operating at high pressure) are typically directed back to the main feed line or cascade tank. While they contribute heat, they are not the primary, sustained *steam* source used for the bulk heating and deaeration process in the DFT. * **B) Low-pressure drains:** Similar to high-pressure drains, low-pressure drains (condensate recovered from devices like fuel oil heaters or LP heaters) are returned to the feed system. They are a source of recovered heat/water but are not the dedicated steam supply needed to continuously maintain the pressure and temperature required for deaeration. * **D) Auxiliary steam:** Auxiliary steam (often referred to as "live" steam, meaning it is taken directly from the boiler or a high-pressure line via a reducing valve) is high-quality, high-cost steam. It is generally used only as a backup (makeup steam) to supplement the auxiliary exhaust system when the exhaust supply is insufficient (e.g., during startup or periods of low auxiliary load). It is not the standard primary heat source because utilizing live steam significantly reduces overall cycle efficiency compared to using recovered exhaust steam.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app