Question 43 OSE02 - Assistant Engineer - OSV
Your platform supply vessel is fitted with cooling water systems serving the main propulsion diesel engines as shown in the illustration. Which heat exchanger/cooler application and aspect would most likely require periodic mechanical cleaning with a specially designed brush? Illustration MO-0137
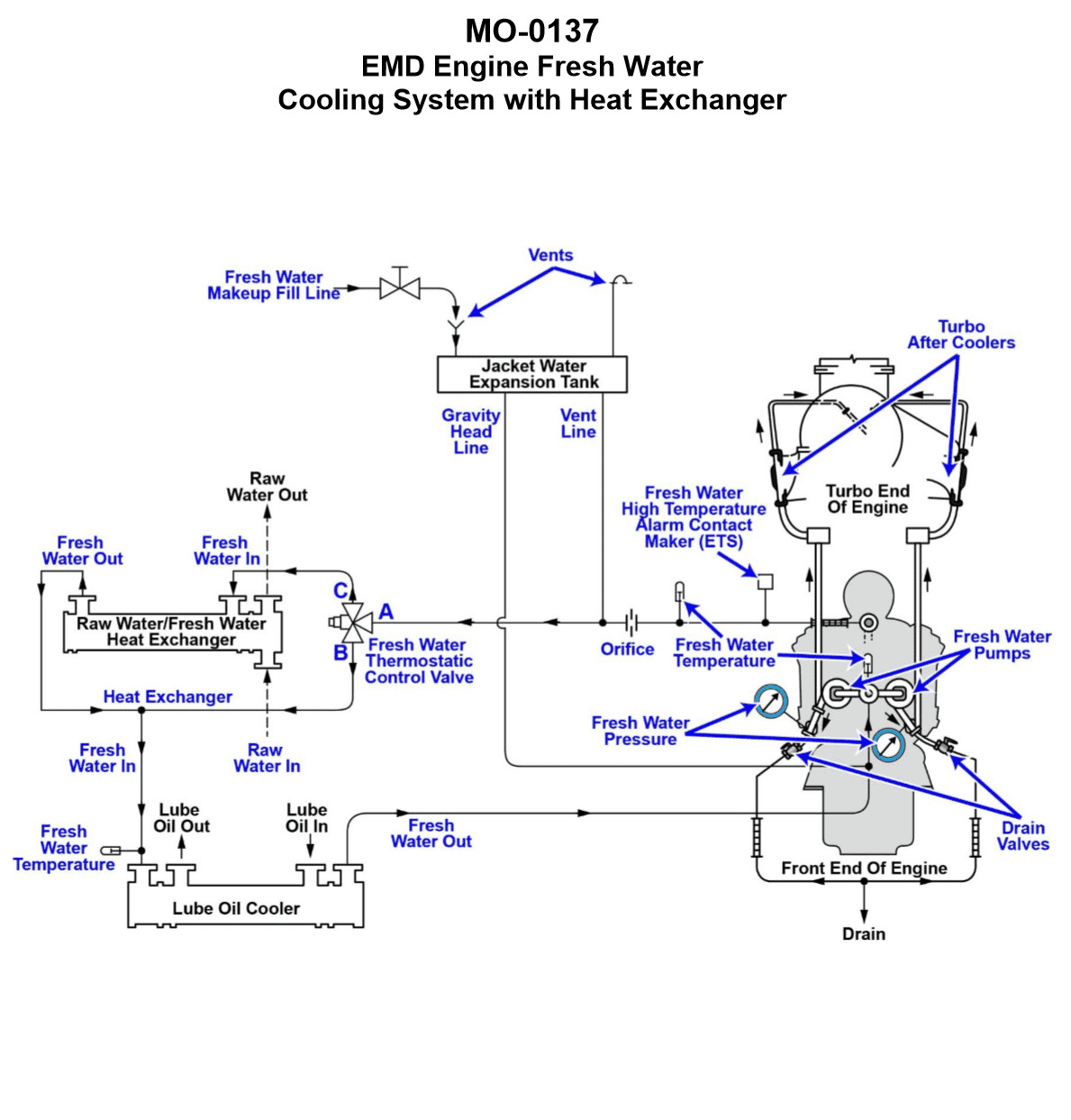
The Correct Answer is D ### Explanation for Option D (Correct) **D) The inside of the tubes of the RW/FW heat exchanger** This option is correct because the RW/FW heat exchanger (often called the Central Cooler) is where the highly corrosive and fouling-prone **Raw Water (RW) or Seawater** transfers heat away from the clean Fresh Water (FW) system. 1. **Flow Configuration:** In a typical marine tubular heat exchanger, the dirtiest fluid flows through the tubes, and the cleaner fluid flows through the shell. Therefore, seawater flows through the inside of the tubes. 2. **Fouling Source:** Seawater contains high concentrations of mineral salts (scaling), silt, sand, mud, and active biological organisms (biofouling/slime). This material rapidly adheres to the internal tube surfaces, reducing heat transfer efficiency. 3. **Cleaning Requirement:** Because the fouling is typically hard (scale) or physical (silt/biofouling), mechanical cleaning using specialized brushes (often driven by water or air pressure) is the standard and most effective periodic maintenance procedure to restore thermal efficiency. ### Explanation for Other Options (Incorrect) **A) The inside of the tubes of the lube oil cooler** The tubes of the lube oil cooler carry the engine lube oil (L.O.). While lube oil can deposit sludge or carbon internally, this type of fouling is usually addressed by chemical cleaning (degreasing/solvent baths) or high-pressure water jetting, rather than routine mechanical brushing designed for removing waterborne scale and biofouling. **B) The outside of the tubes of the RW/FW heat exchanger** The outside of the tubes (the shell side) carries the **Fresh Water (FW)**, which is the closed-loop jacket cooling water. This water is usually chemically treated (inhibited) and filtered, making it very clean. Fouling on the shell side of this exchanger is minimal, thus rarely requiring mechanical brushing. **C) The outside of the tubes of the lube oil cooler** The outside of the tubes (the shell side) of the lube oil cooler carries the **Fresh Water (FW)**. As explained in B, this closed-loop cooling water is clean and treated, minimizing scaling or fouling on the external tube surfaces. Mechanical cleaning is not typically required here.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app