Question 36 MODE02 - Assistant MODU Engineer
The pneumatic propulsion control system used on your vessel uses a diaphragm-operated relay valve as shown in the illustration. Periodically, the valve is to be disassembled for cleaning and inspection. What statement best describes the proper technique? Illustration MO-0052
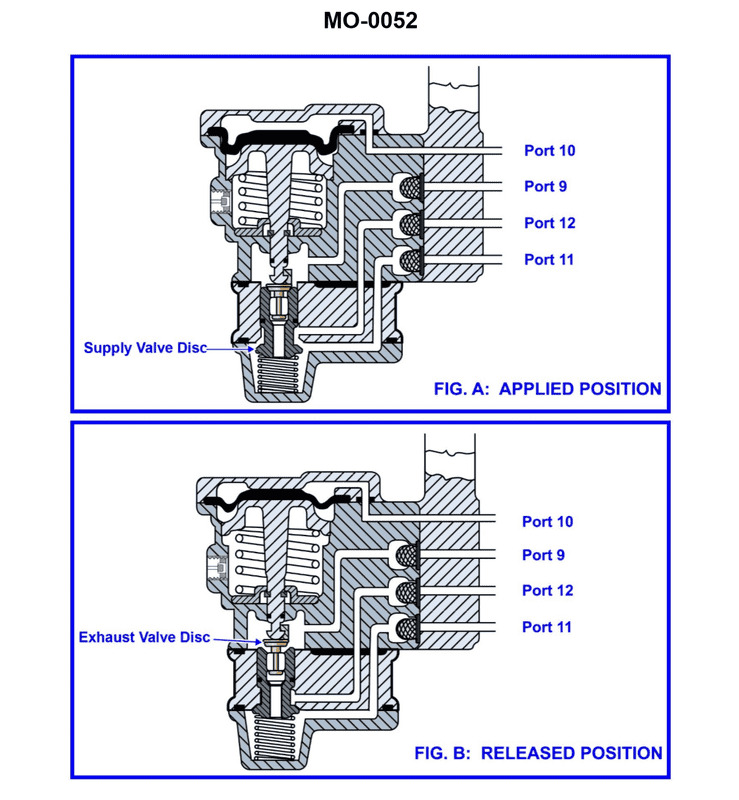
The Correct Answer is B **Explanation of Correctness (Option B):** Option B provides the best practice for cleaning components in a diaphragm-operated pneumatic relay valve. 1. **Rubber Parts (Diaphragm):** Diaphragms are typically made of synthetic rubber or elastomer material. These materials are sensitive to harsh solvents (especially petroleum-based or highly volatile ones), which can cause them to swell, degrade, lose flexibility, or crack. The recommended cleaning method for rubber parts is washing gently with mild soap and water, followed by careful drying. 2. **Metal Parts (Valve Discs and Seats):** Metal parts, such as the valve body, discs, and seats, often accumulate hardened deposits, oil residue, and fine particulate matter. A non-flammable solvent (like specialized industrial cleaning fluids or degreasers, or sometimes isopropyl alcohol depending on the application) is highly effective at dissolving these residues quickly without leaving residue themselves, ensuring a perfectly clean sealing surface for reliable valve operation. **Explanation of Incorrect Options:** * **A) Rubber parts such as the diaphragm and metal parts such as the valve discs and seats should all be washed with soap and water.** While safe for rubber, soap and water are often insufficient for removing tenacious oil, grease, or sticky deposits from precision metal seating surfaces, potentially leaving residues that could interfere with sealing or cause sticking. * **C) Rubber parts such as the diaphragm and metal parts such as the valve discs and seats should all be cleaned with non-flammable solvent.** Using solvents on rubber parts (the diaphragm) poses a significant risk. Even "non-flammable" industrial solvents may contain chemicals that attack, soften, or swell the rubber material, leading to premature failure, loss of responsiveness, or inaccurate control. * **D) Rubber parts such as the diaphragm should be cleaned with non-flammable solvent, and metal parts such as the valve discs and seats should be washed with soap and water.** This option reverses the correct procedures. Cleaning the rubber diaphragm with solvent is hazardous (as noted above), and cleaning the metal seating surfaces with only soap and water is generally ineffective for thorough degreasing and deposit removal.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app