Question 31 DDE04 - Designated Duty Engineer - 1000-4000 HP
The freshwater cooling systems serving the main engines of your towing vessel are of the type shown in the illustration. What statement accurately describes the characteristics of the freshwater cooling circuit? Illustration MO-0137
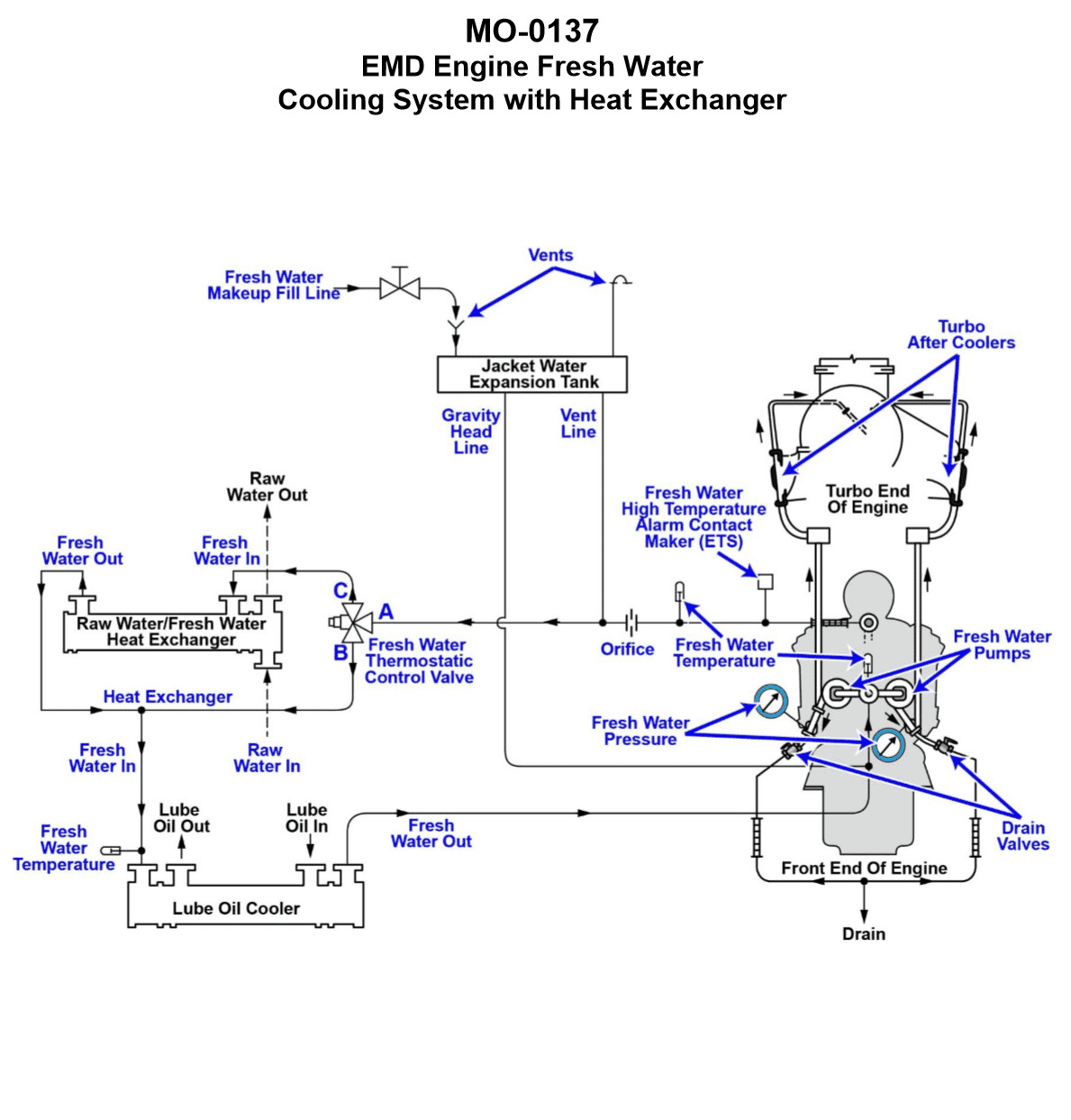
The Correct Answer is C ### Explanation of Why Option C is Correct Option C accurately describes the typical characteristics of a closed freshwater cooling system for medium to large marine diesel engines, especially in vessels like towing vessels, as often depicted in standard marine engineering illustrations (such as those referenced in Coast Guard exams or training materials like MO-0137). 1. **Vented System:** Marine cooling systems that rely on a header tank (surge tank or expansion tank) that is open to the atmosphere (or only slightly above atmospheric pressure via a small vent line) are classified as **vented systems**. This design allows for expansion and contraction of the coolant without building up significant pressure, which is characteristic of engine cooling systems that use heat exchangers (keel coolers or shell-and-tube). 2. **Stationary/Marine Type 3-Way Thermostatic Control Valve:** Temperature control in these main engine cooling circuits is achieved using a regulating valve that modulates the flow of coolant. The typical marine design uses a **3-way valve** (sometimes called a mixing or diverting valve). This valve controls the temperature by diverting a portion of the hot coolant *around* the heat exchanger (bypass) and mixing it with the cooled coolant returning from the heat exchanger, ensuring the engine jacket water maintains a steady, optimal temperature. ### Why Other Options Are Incorrect **A) The freshwater circuit is a pressurized system using a stationary/marine type 3-way thermostatic control valve for temperature control.** * **Incorrect:** While it correctly identifies the 3-way valve, the system is typically **vented** (open to the atmosphere via the header tank) rather than pressurized. High-pressure radiator caps associated with automotive pressurized systems are generally not used in these industrial marine systems. **B) The freshwater circuit is a pressurized system using an automotive type 2-way thermostatic control valve for temperature control.** * **Incorrect:** This is wrong on both counts. The system is vented, not pressurized. Furthermore, it uses a sophisticated **3-way control valve** (or regulator) to modulate the flow, not a simple **2-way automotive-style thermostat** (which merely opens or closes based on temperature). **D) The freshwater circuit is a vented system using an automotive type 2-way thermostatic control valve for temperature control.** * **Incorrect:** While the system is correctly identified as **vented**, it incorrectly specifies the use of an automotive type **2-way thermostatic control valve**. The critical temperature regulation function in a main engine marine system is handled by a 3-way regulating valve.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app