Question 29 DDE04 - Designated Duty Engineer - 1000-4000 HP
The harbor tug to which you are assigned has main engines fitted with intake and exhaust systems as shown in the illustration. What type of turbo-charging configuration is used? Illustration MO-0076
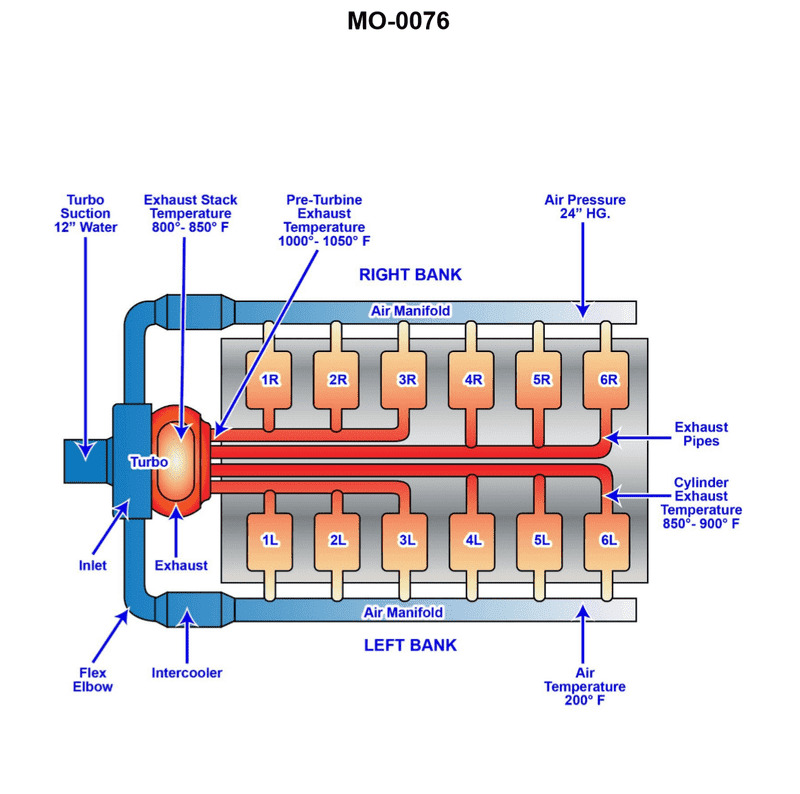
The Correct Answer is D **Explanation for Option D (Pulse turbocharging):** Pulse turbocharging (also known as pressure-wave turbocharging or partial-admission turbocharging) is characterized by the use of an exhaust manifold system designed to maintain and utilize the kinetic energy and pressure pulses generated when the exhaust valves open. In a typical pulse system, the exhaust from a small number of cylinders (often two or three) is grouped into separate, small-volume manifolds (or "pipes") that lead directly to the turbine inlet. These inlets are often separated by partitions (pulse-converting nozzles) in the turbine housing (making it a twin or triple-entry turbine). If Illustration MO-0076 depicts short, distinct exhaust pipes leading from cylinder groups directly to a divided turbine inlet, it indicates that the system is engineered to capture and exploit the high-energy pressure pulses. This design provides better turbocharger response at lower engine loads compared to constant pressure systems, making it a very common configuration for medium and high-speed four-stroke diesel engines, such as those found in harbor tugs. **Why the other options are incorrect:** * **A) 2-stage turbocharging:** This configuration involves the air being compressed sequentially by two separate turbochargers (a high-pressure stage and a low-pressure stage) to achieve extremely high boost pressures. While highly efficient, this description relates to the overall compression process, not the specific design of the exhaust manifold/turbine entry illustrated by the choice between pulse and constant pressure systems. The illustration must show the specific manifold arrangement (separated pipes vs. large common manifold) to distinguish the configuration. * **B) Boost-controlled turbocharging:** This term refers to a control mechanism (like a wastegate or variable turbine geometry) used to limit or regulate the maximum boost pressure, especially at high engine speeds. It is a control feature, not the fundamental classification of the manifold and turbine inlet design (pulse vs. constant pressure). * **C) Constant pressure turbocharging:** This system uses a large-volume exhaust manifold (plenum) that collects the exhaust gases from all cylinders, damping out the individual pressure pulses before the gas reaches a single-entry turbine. The gas enters the turbine at a relatively steady (constant) pressure, utilizing thermal energy more efficiently but suffering from slower response at low loads. If the illustration shows short, separated pipes (as required for D), then it cannot be a constant pressure system.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app