Question 6 UFIV02 - Assistant Engineer - UFIV
You are assigned as an engineer on a fishing research vessel using main propulsion engines of the type shown in the illustration. What statement represents the procedure for inspection of the upper cylinder liner bore while in place inside the engine? Illustration MO-0122
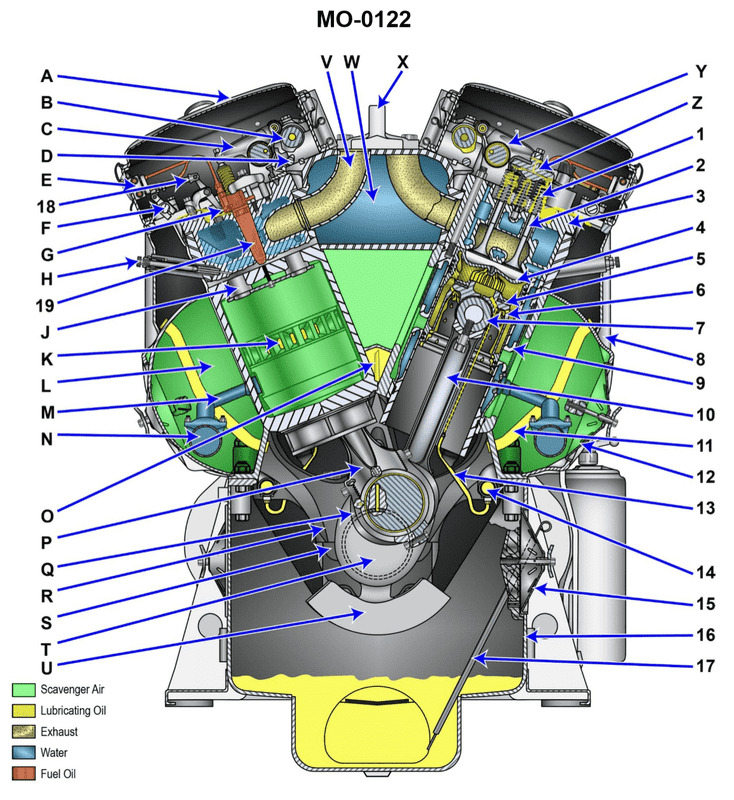
The Correct Answer is C ### Why Option C is Correct Option C states: "With the particular piston positioned at BDC and the corresponding air box handhole cover removed, inspect the upper liner bore through the scavenging air ports." 1. **Inspection Target:** The goal is to inspect the "upper cylinder liner bore." This is the area most subject to wear and thermal stress, specifically the ring travel area near the combustion space. 2. **Access Method:** On engines (especially two-stroke types like the one often implied by "scavenging air ports," such as some EMD or large marine diesels), inspection of the liner walls is commonly done through the scavenging air ports located around the lower part of the liner. 3. **Piston Position (BDC):** To inspect the *upper* part of the liner (where the rings run at TDC), the piston must be moved out of the way. When the piston is at Bottom Dead Center (BDC), the entire working surface of the liner, including the critical upper area, is exposed above the scavenging ports, allowing light and visual access through the ports. 4. **Cover Removal (Air Box):** The scavenging air ports are fed by the air box (also known as the scavenging receiver). To gain visual access to these ports from outside the engine, the air box handhole cover (sometimes called the scavenging belt cover) must be removed. ### Why Other Options Are Incorrect **A) With the particular piston positioned at TDC and the corresponding oil pan handhole cover removed, inspect the upper liner bore through the scavenging air ports.** * **Piston Position:** Placing the piston at Top Dead Center (TDC) completely covers the critical upper liner area, preventing inspection. * **Cover Removal:** Inspecting through scavenging ports requires removal of the **air box** cover, not the oil pan cover. **B) With the particular piston positioned at BDC and the corresponding oil pan handhole cover removed, inspect the upper liner bore through the scavenging air ports.** * **Cover Removal:** While the piston position (BDC) is correct for exposing the upper liner, inspecting through the scavenging ports requires removing the **air box** cover, not the oil pan (crankcase) cover. **D) With the particular piston positioned at TDC and the corresponding air box handhole cover removed, inspect the upper liner bore through the scavenging air ports.** * **Piston Position:** Placing the piston at Top Dead Center (TDC) blocks the upper liner area from view and measurement.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app