Question 3 UFIV02 - Assistant Engineer - UFIV
You are assigned to a fishing factory ship fitted with main propulsion diesel engines of the type shown in the illustration. If the engine's crankshaft is turning at 720 rpm, what will be the rotational speed of the two camshafts? Illustration MO-0005
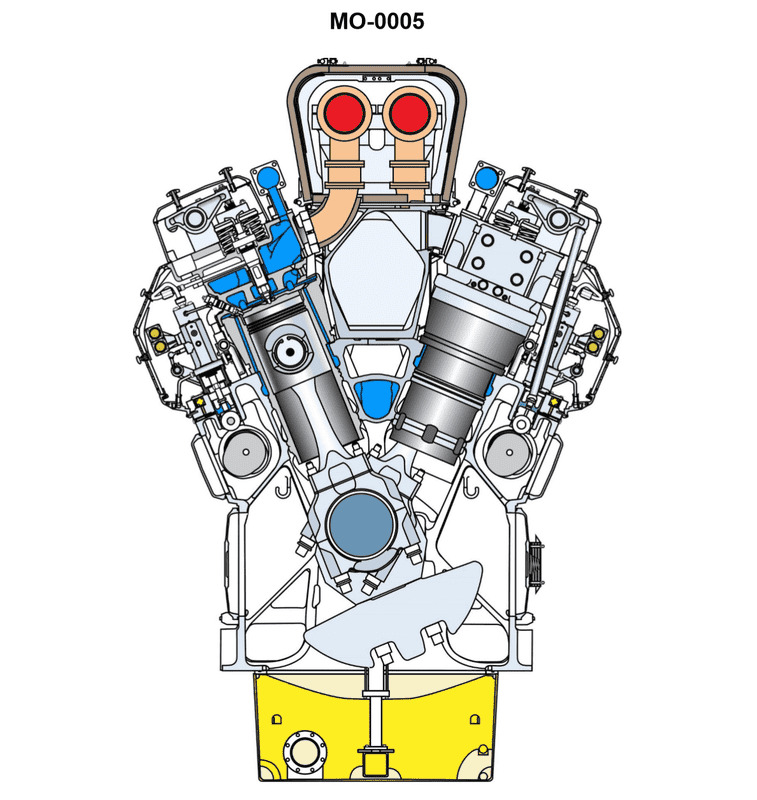
The Correct Answer is A. ### Explanation of Correctness (Option A: 360 rpm) The fishing factory ship is fitted with a marine diesel engine. While Illustration MO-0005 is not provided, the configuration described (main propulsion diesel engine with two camshafts) almost certainly refers to a standard four-stroke internal combustion engine cycle. In a **four-stroke engine**, the piston completes four distinct strokes (Intake, Compression, Power, Exhaust) for every single power cycle. The crankshaft must rotate **two full revolutions (720 degrees)** to complete this cycle. The camshaft's purpose is to actuate the intake and exhaust valves at the correct time during this four-stroke cycle. Since the valves only need to open once per cycle (which corresponds to two crankshaft revolutions), the camshaft must rotate only **one full revolution (360 degrees)** for every two revolutions of the crankshaft. Therefore, the gear train connecting the crankshaft to the camshaft is designed with a **2:1 reduction ratio**. * Crankshaft Speed = 720 rpm * Camshaft Speed = Crankshaft Speed / 2 * Camshaft Speed = 720 rpm / 2 = **360 rpm** This principle holds true regardless of whether the engine has one camshaft or two, as both camshafts must operate synchronously with the engine cycle. *** ### Explanation of Incorrect Options **B) 720 rpm:** This would mean the camshaft is turning at the same speed as the crankshaft (1:1 ratio). In a four-stroke engine, this would cause the valves to open twice as often as needed, leading to catastrophic engine failure because the timing would be completely incorrect (e.g., opening the exhaust valve during the intake stroke). **C) 1440 rpm:** This would mean the camshaft is turning twice as fast as the crankshaft (1:2 ratio). This is physically impossible in a standard four-stroke design where the camshaft controls the timing dictated by the crankshaft's two revolutions per cycle. **D) Not enough information is given to determine camshaft rpm:** Sufficient information is given. The type of engine ("main propulsion diesel engine") dictates the four-stroke cycle, and the four-stroke cycle mandates a fixed, non-negotiable 2:1 reduction ratio between the crankshaft and the camshaft. No further information (like gear size, bore, or stroke) is needed.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app