Question 2 QMED04 - Boiler Technician-Watertender
While underway on a steamship, the main condenser is operating under a 28.09 "Hg vacuum gauge. According to the illustrated properties of saturated steam table, how much condensate depression would there be if the condensate temperature leaving the main condenser hot well is 96.0°F? Illustration SG-0026
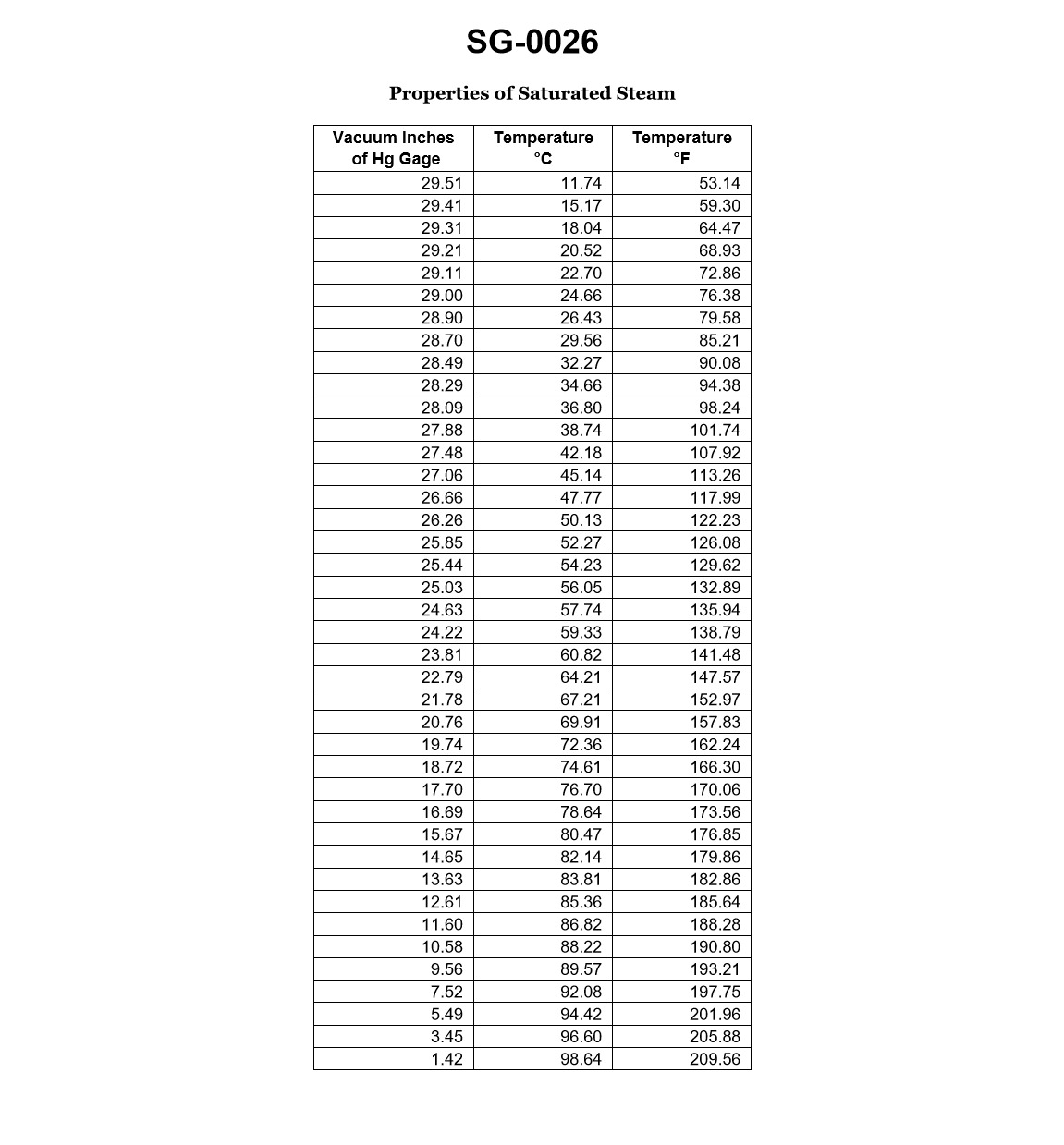
The Correct Answer is B ### 1. Explanation for Option B (2.24°F) The required value is the **condensate depression**, which is the difference between the saturation temperature corresponding to the condenser vacuum and the actual temperature of the condensate leaving the hotwell. **Formula:** $$\text{Condensate Depression} = T_{\text{saturation}} - T_{\text{condensate}}$$ **Step 1: Determine the Absolute Pressure in the Condenser.** The condenser vacuum is given as $28.09 \text{ "Hg (gauge)}$. To use the saturated steam table (which correlates saturation temperature to absolute pressure), we must first find the absolute pressure. Assuming standard atmospheric pressure (for typical maritime/engineering contexts) is $29.92 \text{ "Hg}$: $$\text{Absolute Pressure} = \text{Atmospheric Pressure} - \text{Vacuum Gauge Reading}$$ $$\text{Absolute Pressure} = 29.92 \text{ "Hg} - 28.09 \text{ "Hg}$$ $$\text{Absolute Pressure} = 1.83 \text{ "Hg}$$ **Step 2: Find the Saturation Temperature ($T_{\text{saturation}}$).** Using the saturated steam table (SG-0026) for an absolute pressure of $1.83 \text{ "Hg}$: The table shows that the saturation temperature corresponding to $1.83 \text{ "Hg (absolute)}$ is $98.24^{\circ}\text{F}$. $$T_{\text{saturation}} = 98.24^{\circ}\text{F}$$ **Step 3: Calculate the Condensate Depression.** The actual condensate temperature ($T_{\text{condensate}}$) is given as $96.0^{\circ}\text{F}$. $$\text{Condensate Depression} = 98.24^{\circ}\text{F} - 96.0^{\circ}\text{F}$$ $$\text{Condensate Depression} = 2.24^{\circ}\text{F}$$ Therefore, the condensate depression is $2.24^{\circ}\text{F}$. --- ### 2. Explanation of Why Other Options are Incorrect **A) 1.83°F** This value is the absolute pressure in the condenser ($1.83 \text{ "Hg}$), not the temperature difference. This option is incorrect because it confuses pressure units with temperature units. **C) 8.71°F** This result is obtained if an incorrect saturation temperature is used. If one mistakenly used a saturation temperature corresponding to a higher vacuum or made a calculation error, this result could arise, but it does not match the thermodynamic properties provided by the pressure $1.83 \text{ "Hg absolute}$. (For example, $104.71^{\circ}\text{F} - 96.0^{\circ}\text{F} = 8.71^{\circ}\text{F}$, where $104.71^{\circ}\text{F}$ is the saturation temperature corresponding to approximately $2.24 \text{ "Hg absolute}$). **D) 70.15°F** This value is far too large for a typical condensate depression. This error likely results from using a completely incorrect reference point, such as calculating the difference between the condensate temperature and $32^{\circ}\text{F}$ or subtracting the vacuum gauge reading from the saturation temperature, which results in a meaningless physical quantity for this calculation.
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app