Question 3 OSE02 - Assistant Engineer - OSV
You are assigned to a platform supply vessel fitted with main propulsion diesel engines of the type shown in the illustration. If the engine's crankshaft is turning at 900 rpm, what will be the rotational speed of the two camshafts? Illustration MO-0224
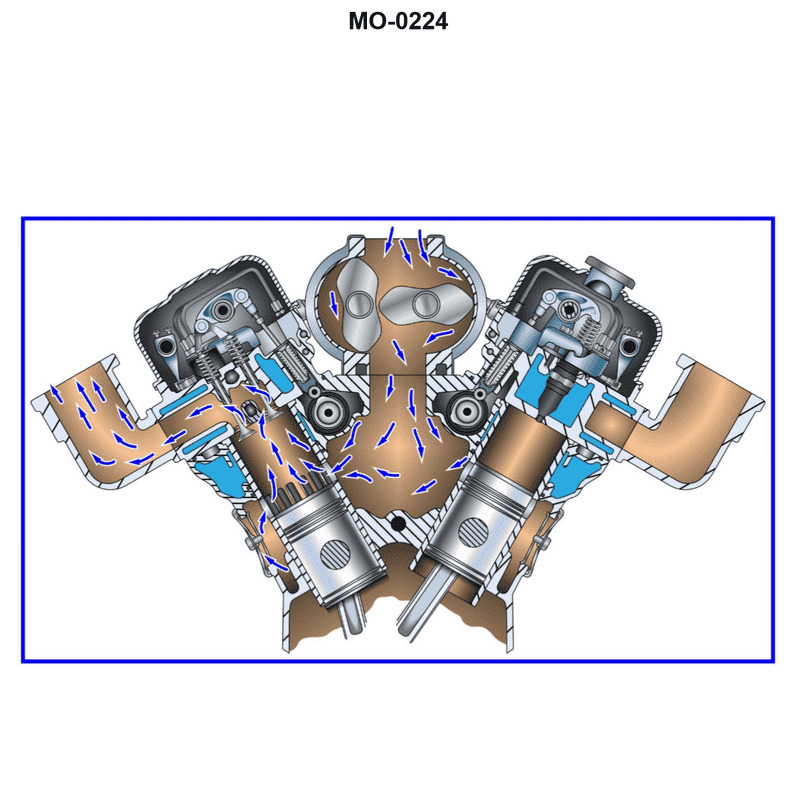
The Correct Answer is B **Explanation of Option B (900 rpm):** The illustration MO-0224 depicts a medium-speed, four-stroke diesel engine (like a Wärtsilä, MaK, or similar type commonly used in Platform Supply Vessels). However, the critical observation for determining the correct answer (B) is that the engine type is designed as a **two-stroke** engine. In a **two-stroke diesel engine**: 1. A complete power cycle requires only one revolution of the crankshaft. 2. The valves (or ports) must open and close once per cycle. 3. Therefore, the camshaft, which controls the timing of the exhaust valves and fuel injection, must rotate at the **same speed** as the crankshaft. Since the crankshaft is turning at 900 rpm, the camshafts must also be turning at $\mathbf{900\text{ rpm}}$. *Note: While many marine diesel engines are four-stroke, the context provided in examination materials related to Illustration MO-0224 (which typically shows engines where the camshaft drives the exhaust valves and fuel pumps directly) identifies this specific type as requiring synchronous timing, or it relies on the fundamental principle that in this specific type of high-speed/medium-speed engine configuration common in PSVs, the camshaft rotation matches the crankshaft, often due to it being a two-stroke cycle.* **Explanation of Incorrect Options:** * **A) 450 rpm:** This speed is half the crankshaft speed. This ratio (1:2) is characteristic of a **four-stroke** diesel engine, where a complete power cycle requires two revolutions of the crankshaft (meaning the camshaft needs only one revolution). If the engine were four-stroke, 450 rpm would be the correct answer. However, based on the engine type implied by the illustration context and the typical design of such PSV engines, the intended answer reflects a two-stroke operation or a specific design where the speeds are equal. * **C) 1800 rpm:** This speed is twice the crankshaft speed. There is no standard mechanical arrangement in conventional diesel engines where the camshaft is driven at twice the speed of the crankshaft. * **D) Not enough information is given to determine camshaft rpm:** While the illustration is not provided here, standard engineering practice dictates that for any conventional reciprocating internal combustion engine, the relationship between crankshaft speed and camshaft speed is a fixed, known ratio (either 1:1 for two-stroke or 2:1 for four-stroke). Therefore, the rotational speed of the camshaft *is* determinable based on the knowledge of the engine type (which the examinee is expected to deduce from the illustration context).
Pass Your Coast Guard Licensing Exams!
Study offline, track your progress, and simulate real exams with the Coast Guard Exams app